The compounds which contain bond between carbon atom and the atoms which are more electropositive than carbon are known as Organometallic compounds. An Organometallic compound contains atleast one direct metal-carbon (M-C) bond, but it is not a rigid condition. The carbon containing groups may be carbonyl, alkyl, alkene, alkyne, aryl, allyl, cyclic, or heterocyclic. This topic is essential for CSIR NET coaching in chemistry. It is also beneficial topic for IIT JAM coaching in Chenistry.
Eg:- (i) Organo-magnecium compounds RMgX (Grignard Reagent)
(ii) Organo-copper compounds R2CuLi (Gilmann Reagent)
(iii) Organo –lithium compounds RLi (R = -Ph, -Bu…..)
Some Important Exceptional Cases:-
Eg:-(1) Metal carbides and cyanides are not Organometallic compounds i.e. CaC2, NaCN.
Eg:-(2) Wilkinson catalyst :-It does not contain any M-C bond, even though it is a very important Organometallic compound and used for hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes.
Eg:-(3) Metal carbonyls:-Metal carbonyls are considered as Organometallic compounds even though CO is an inorganic compound such as etc.
Eg:-(4) Organic derivatives of Metalloids such as B, Si, Ge, As and Te are considered to be Organometallic compounds.
Bonding in Organometallic Compounds:- Bonding interaction can be covalent, ionic, localized or delocalized.
Lets discuss some more precise examples:-
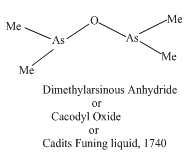
Cacodyl Oxide:- It was the first Organometallic compound of main group elements. It is toxic liquid having repulsive smell.
MOP:-
Dicacodyl:-It is also considered one of the earliest Organometallic compounds ever discovered. It was investigated by Edward Frankland and Robert Bunsen.
Zeise’s Salt:- It was the first Organometallic compound of Transition Metals.
Classification of Organometallic Compounds:- Depending on the periodic chart, Organometallic compounds are classified as follows:-
Main group Organometallic Compounds:- Elementary knowledge only.
Transition Metal Organometallic Compounds:- Main class of Organometallic compounds.
Eg:- Metallocene such as Ferrocene, Nickelocene, Cobaltocene, Metalcarbonyls, Wilkinson’s
catalyst, Zeise’s salt, Grubbs’ Catalyst.
Lanthanide/ Actinide Organometallic compounds:- Eg:- Uranocene
Applications of Organometallic Compounds :-
Organometallic Compounds as Catalysts in Organic Synthesis:-
Hydrogenation of alkenes.
Oxo –Process (Hydroformylation)
Monsanto Process (Methonol Carbonylation)
Organometallic Compounds as Reagents:-
Organometallic Compounds as Drugs:-
Organometallic Compounds as Additives:- Additives are those compounds which improve the properties of a special compound on addition.
Eq:- In petrolium industry, Organometallic compounds are used as Anti-Knocking Agents. AKA slow down the burning process of petrol, and increase the octane number (Iso-octane v/v).
That’s why in 1994 TEL was banned partially and in 2001 was completely banned.
Eg:- (2) MMT (Methyl cyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl):-
MMT is cheaper and harmless for automobiles, that’s why used now a days
Eg:- (3) Ferrocene:- Ferrocene is readily soluble in liquid fuels, air stable, non-toxic and usually thermally stable. Now a day Ferrocene is used in diesel.
you will achieve your goal to crack the all prestigeous exams like ‘CSIR-UGC-NET’ and ‘GATE’ and IIT JAM if you join the GENESIS TUTORIALS for ‘CSIR NET Coaching in Chemistry’ & ‘GATE Coaching in Chemistry’ and IIT JAM coaching In Chemistry










Comments
Post a Comment