From the exam point of view like CSIR-UGC-NET in Chemistry, JAM in Chemistry and GATE in Chemistry, Coordination Chemistry is very important branch of chemistry. Therefore many questions are asked from Coordination Chemistry in NET in Chemistry and JAM in Chemistry. Hence we can say that it is the hot topic for NET coaching in Chemistry’. Not only for NET, it is also key topic for JAM coaching in Chemistry.
The competitive exam level is very much high now a days because all the fields having good opportunities are full of students and are more demanding. So the students should be ready for cracking competitive exams for bright future. But the number of seats remains constant so it is the big challenge for every students to get success in the competitive exams. Since NET coaching in Chemistry, JAM coaching in Chemistry providing by different institute solves the problems of students and modify them according to the competitive exams. Therefore if you want to get some competitive key then you should join these institutes for the best career in the field of Chemistry and Chemical Sciences.
All students have a dream to take an admission in Ph.D./M.Tech./M.Sc. programme in Chemistry in the prestigious institute IITs, NITs and prestigious Universities, but this dream is true only through ‘NET coaching in Chemistry’ & ‘JAM coaching in Chemistry.
The competitive exam level is very much high now a days because all the fields having good opportunities are full of students and are more demanding. So the students should be ready for cracking competitive exams for bright future. But the number of seats remains constant so it is the big challenge for every students to get success in the competitive exams. Since NET coaching in Chemistry, JAM coaching in Chemistry providing by different institute solves the problems of students and modify them according to the competitive exams. Therefore if you want to get some competitive key then you should join these institutes for the best career in the field of Chemistry and Chemical Sciences.
All students have a dream to take an admission in Ph.D./M.Tech./M.Sc. programme in Chemistry in the prestigious institute IITs, NITs and prestigious Universities, but this dream is true only through ‘NET coaching in Chemistry’ & ‘JAM coaching in Chemistry.
Valence Bond Theory
- Acc. to VBT complex formation is done is done in 3 steps.
- Control metal ion provide as many as s, p and d orbital which is equal to its coordination no.
- This vacant orbital hybridized though to give equal no. of hybrid orbital which are equivalent energetically, symmetrically stereo chemically and directed in a particular direction.
- Ligand provide e- pair to each hybrid orbital forming a special type of covalent bond called as coordinate covalent bond represented by [] Arrow head point towards M.
After complex formation μ =0
Magnetic
moment will decide is this theory is correct not. By magnetic moment instrument
μ is found to be equal O.
Whenever μ decrease with complex formation
resulting complex is low spin. Both w.r.t free metals.
Low
spin High
spin
Spin
paired complex spin free complex
Hypo
– Ligated Hyper – Ligated
Decrease μ remain same
Back
pairing of electron is thermodynamically unfavorable process. Violation of
Hund’s rule
It
requires energy for pairing of electron.
If
Ligand are electron donor Si, S, P, C N(Sp3) they are highly
polarizable associated with low electro negativity – So, donate electron
strongly forming very strong covalent bond and energy release is able to compensated energy
required for pair. But if Ligand is non – polarizable associated with high
electro negativity like O, F N (sp2 sp) donor. They only from very
weak bond X (halogen)
So,
energy released is not sufficient for pairing & they form bond of high
energy at outermost d – orbital.
Similar
thing is observed in C.N = 4 i.e.
Strong
donor Ligand from square planer complex
Weak
donor Ligand from tetrahedral complex
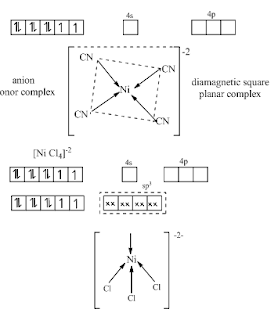
[Ni
(CN) 4]-2
All
tetrahedral complexes are always high spin because d orbital are unaffected.
If
in C.N = 4 square planer complex is formed than is low spin [Fe L6]
+μ = 5.93 BM
neutral
L →
Drawback of VBT
Octahedral
of complexes of configuration d0-3 & d8 – 10 connect
be distinguished as high spin or low spin complexes simply on the basis of
magnetic moment.
Similar case is observed with square
planar complexes also.
VBT
is able to explain magnetic property of complex but unable to explain colour
property of complex.
However
these are strong relationship between magnetic & coloured properties.
Generally
diamagnetic complexes are colorless e.g. off white, pale colour paramagnetic
complexes are generally strong coloured.
VBT
is unable to understand the relationship between magnetic & spectral
property.
VBT
is strongly biased towards coordination no Co & 4 all the octahedral
complex of Ni with strong donor Ligand are unstable & change into
coordination no 4 losing two Ligands.
[Ni
(NH3) 6]+3  [Ni (CH3)4]2+
= 2NH3
[Ni (CH3)4]2+
= 2NH3
[Ni
(CH3) 5] is more stable than [Ni (NH3) 4]
+2 but still acc. to VBT 2NH3 will be loosed.
It
is completely failed in explaining structure & hybridization of
[Cu (NH3)4]+2
By
X – ray technique it got cleared that this complex is square planar.
All
Co2+ with strong Ligand are unstable and oxidies i.e. immediately
changes to +3.
VBT explanation [Co (NH3) 6]
+2 Co2+ is
highly unstable in ammonia.
Acc.
to VBT single e- in 4d is highly unstable, so, [Cu (NH3)4]
+2 should be highly unstable acc. to VBT. But it is highly stable.
Most
acceptable hybridization is outer orbital but exact stability of [Cu (NH3)4]
+2 is not known to VBT. So, we need another theory that is Crystal
field theory (CFT).





Comments
Post a Comment